Ansible AWX
It has been a while as I have been busy writing, I thought I would spend some of my freetime having a very quick play with Ansible AWX, which is the Open Source version of Ansible Tower.
I created the following Vagrantfile to launch a CentOS 7 server;
# -*- mode: ruby -*-# vi: set ft=ruby :
VAGRANTFILE_API_VERSION = "2"
Vagrant.configure(VAGRANTFILE_API_VERSION) do |config| config.vm.box = "centos/7" config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |v| v.memory = 4048 v.cpus = 2 v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--natdnshostresolver1", "on"] v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--ioapic", "on"] end config.vm.define "awx" do |awx| awx.vm.hostname = "awx.local" awx.vm.network :forwarded_port, guest: "80", host: "8080" awx.vm.provision :ansible do |ansible| ansible.playbook = "playbook.yml" ansible.become = true end end
endThis launches the following playbook.yml which prepares the CentOS 7 box by installing Docker and the other prerequisites need to build and launch AWX;
- name: Deploy AWX hosts: all become: true become_user: root
tasks:
- name: sort out the yum repos yum: name: "{{ item }}" state: "latest" with_items: - "epel-release" - "yum-utils"
- name: add the docker ce yum repo yum_repository: name: "docker-ce" alt: "Docker CE YUM repo" gpgcheck: "yes" enabled: "yes" baseurl: "https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/7/$basearch/stable" gpgkey: "https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/gpg"
- name: install the prerequisites using yum yum: name: "{{ item }}" state: "latest" with_items: - "epel-release" - "libselinux-python" - "python-wheel" - "python-pip" - "git" - "docker-ce"
- name: start and enable docker systemd: name: "docker" enabled: "yes" state: "started"
- name: install the python packages using pip pip: name: "{{ item }}" state: "latest" with_items: - "pip" - "ansible" - "boto" - "boto3" - "docker"
- name: check out the awx repo git: repo: "https://github.com/ansible/awx.git" dest: "~/awx" clone: "yes" update: "yes"
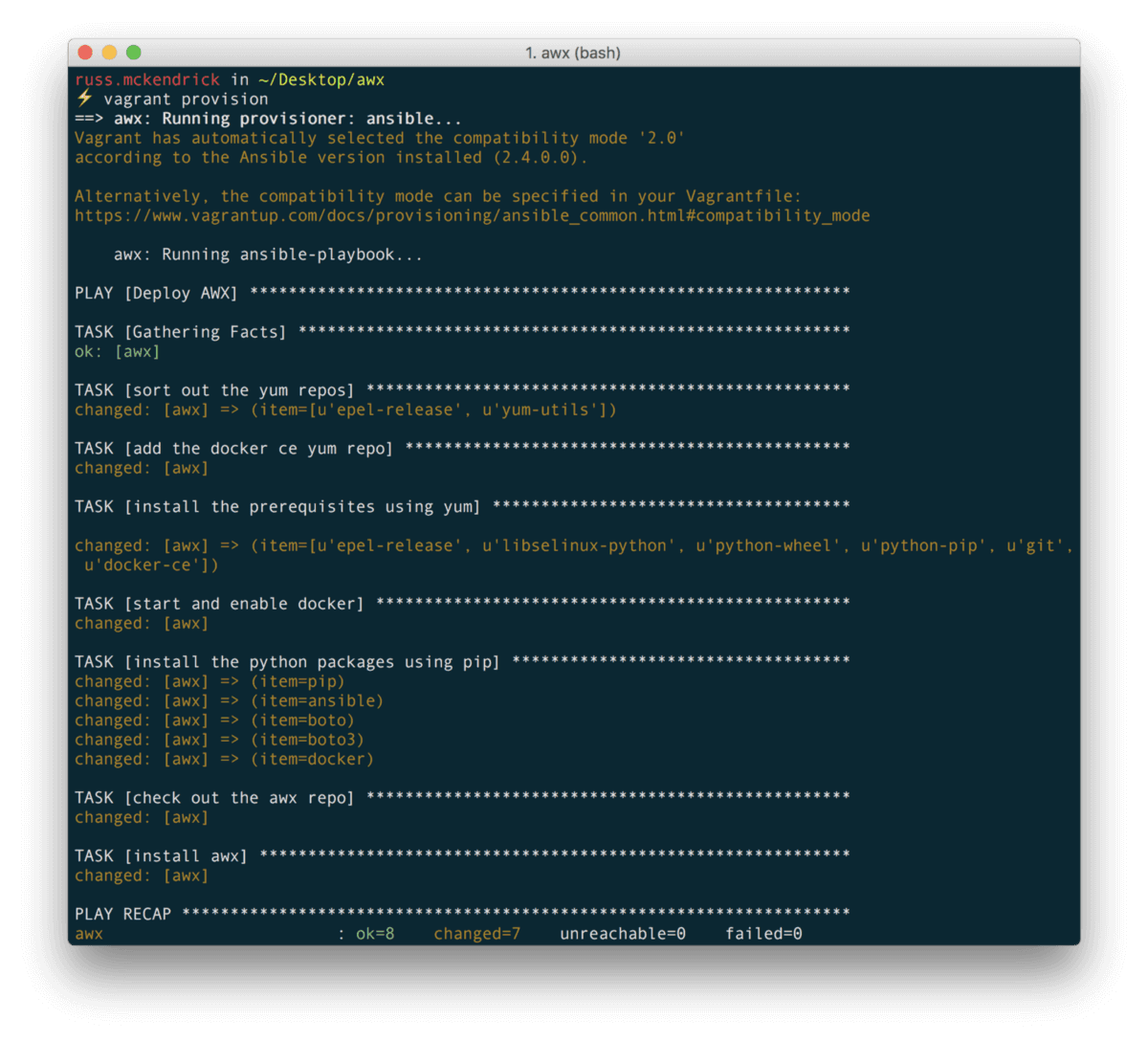
- name: install awx command: "ansible-playbook -i inventory install.yml" args: chdir: "~/awx/installer"(You can find the files above in a gist on GitHub) Running vagrant up will launch the CentOS 7 machine and execute the playbook to install AWX, this process takes about 15 minutes.
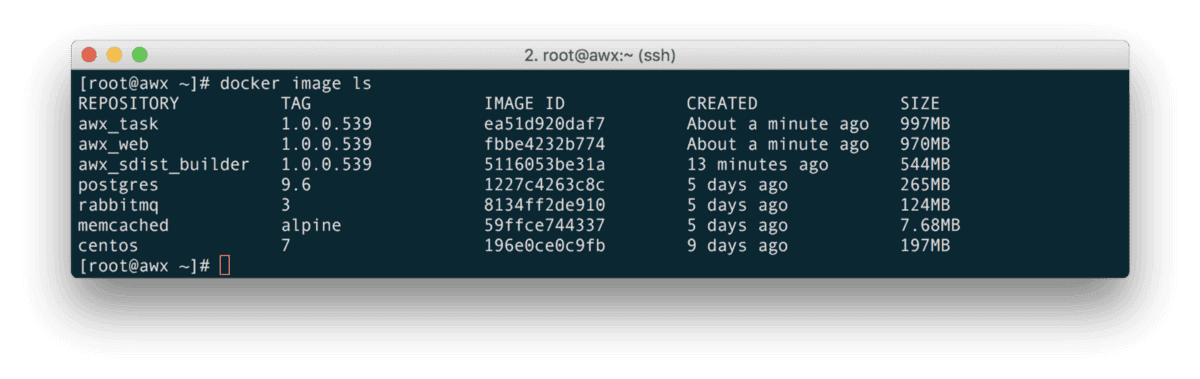
In the background the installer has built and downloaded several Docker images, you can check what is going on the machine by running;
vagrant sshsudo docker image lssudo docker container lsOnce the build has completed you should the following images;
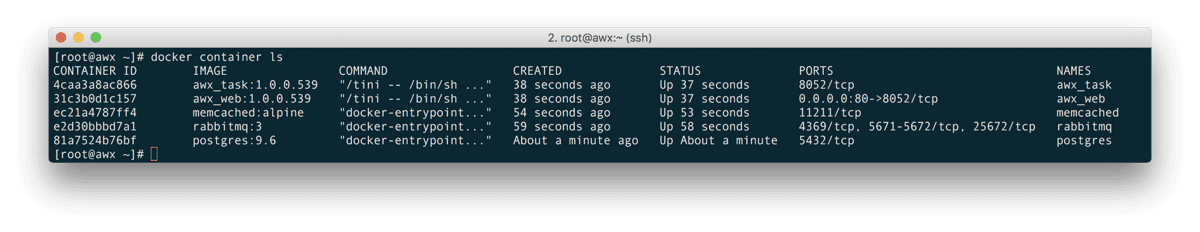
Also, you should have several containers running;
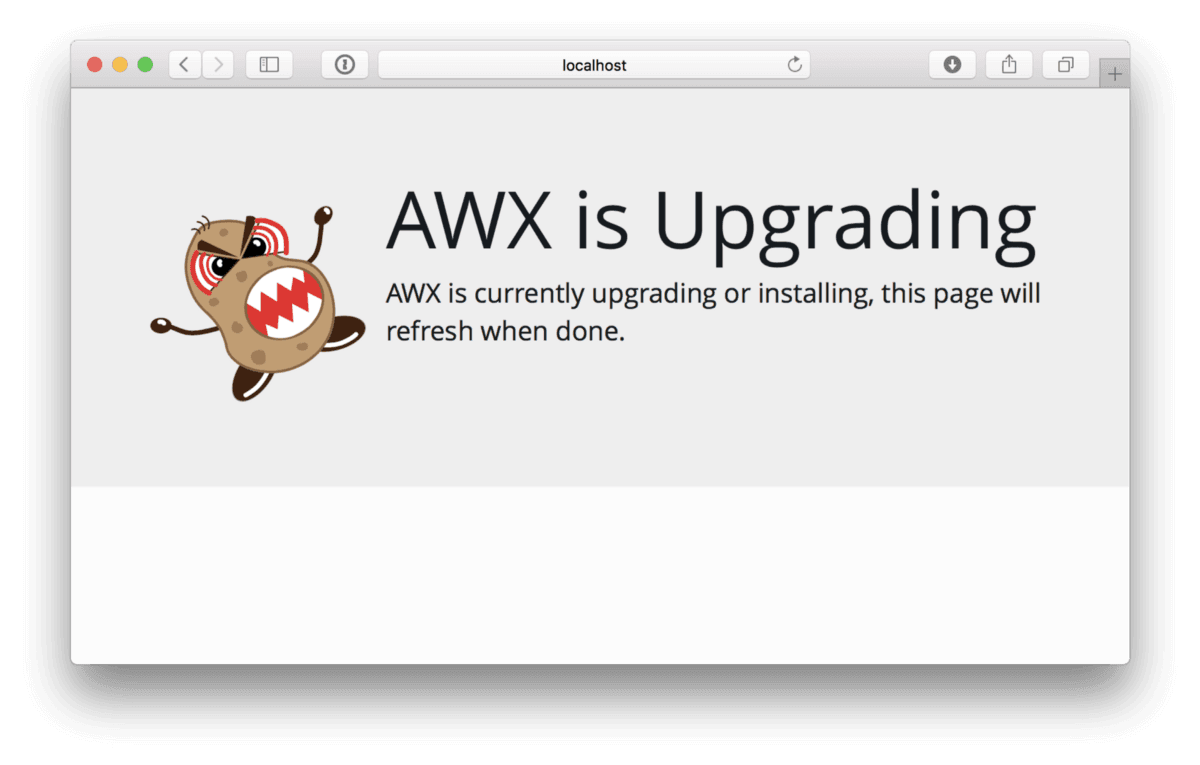
Once the containers have launched, going to http://localhost:8080/ should show you the following;
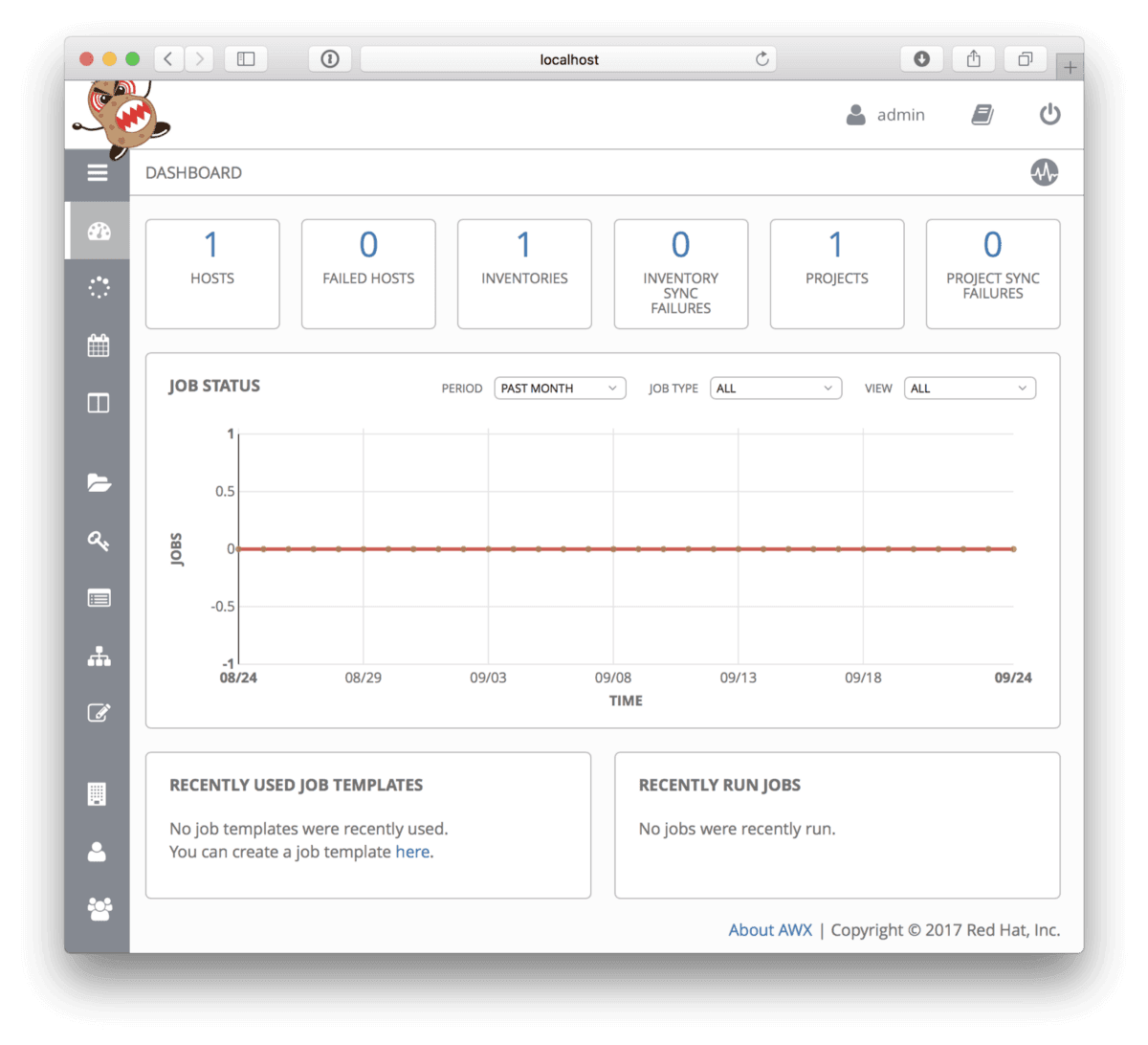
After a while the page will eventually refresh into a login screen, the default user is admin and the password is password. Once logged in you will be taken to the dashboard, here you can see that there is already a project created, this is a simple test job;
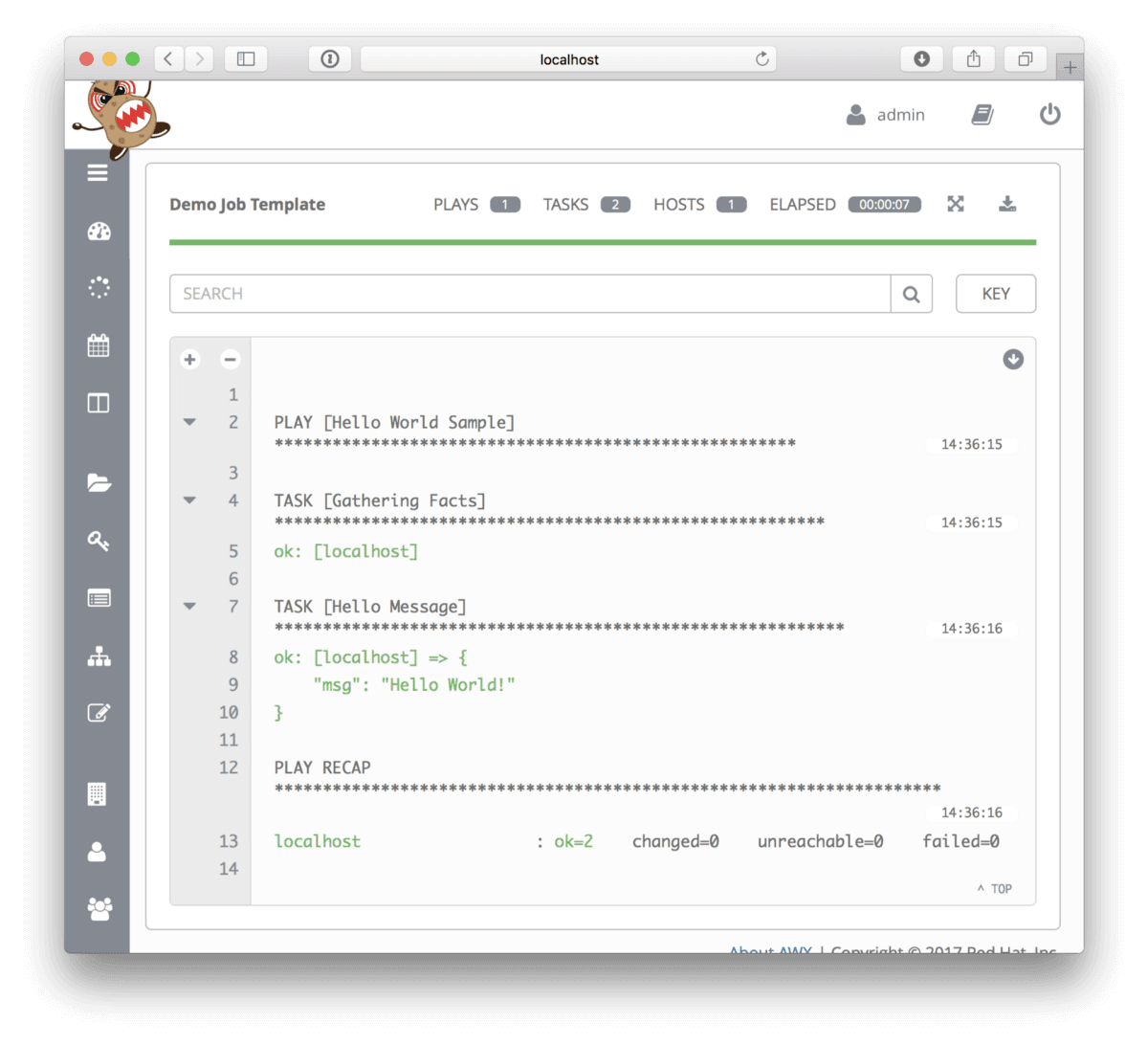
You can test your installation by running the test job, which is the Ansible equivalent of a Hello World, you can see the output of running the template below;
As I said at the start of this post this was a only a quick post to document how you can get quickly (well sort of quickly) get an AWX host up and running, if you would like more detail on how to use AWX see the Ansible Tower Document site.
Share
Related Posts

First Steps with Ansible
Explore Ansible for AWS automation, transitioning from manual scripting. Initiate playbook for VPC and ELB deployment.

Azure DevOps Ansible Pipeline
Streamline your DevOps workflows by setting up an Azure pipeline using Ansible playbooks. Learn how to integrate Azure CLI for faster results!

Jenkins
Discover Jenkins for automation on CentOS 7 with NGINX SSL setup. Orchestrate tasks efficiently!