Adding a SSH Key to Azure
In my previous post I wrote about launching a CentOS 7 Virtual Machine in Azure using Terraform.
As you can see from my original configuration I was adding a password and my own user. This worked well, the machine launched and I could access it as expect and sudo to root.
However, when it came to using Terraforms built-in provisioner I started to have problems as the commands I was running need root privileges, when I tried using sudo it would sit there waiting for the password to entered.
After doing a little reading I found that if I was to launch the Virtual Machine with a SSH Key I would be able to get passwordless sudo access.
Checking through Terraform documentation it hinted that I could use an uploaded key when launching the VM by using the ssh_key_thumbprint variable. Great, where do I upload my key?
A few hours and much head scratching later I had it sorted.
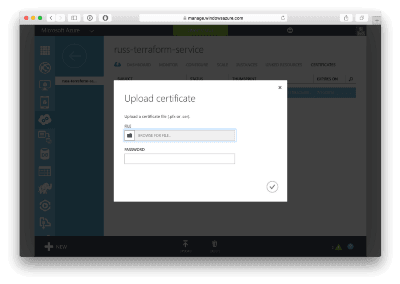
First of all, you don’t upload keys. Instead, you will need to convert your key to pem file and then a certificate. You can do that using the commands below (replace the paths as needed);
openssl req -x509 -key /.ssh/id_rsa -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -out /Desktop/myCert.pem openssl x509 -outform der -in ~/Desktop/myCert.pem -out ~/Desktop/myCert.cerOnce you have your certificate file it’s time to upload it. This is where things got confusing, the only obvious place I could find clicking around the interface was Settings -> Management Certificates which made complete sense to me coming from an AWS background. I uploaded it, launched my Virtual Machine using Terraform and it failed to find the thumbprint so it was back to Google.
After a while I realised as I was launching my Virtual Machine into a “Cloud Service” and that I had to add the certificate there.
Once I had uploaded the certificate to the Cloud Service I was able to launch the Virtual Machine using the ssh_key_thumbprint variable, the provisioner was able to connect and finally execute sudo without having to provide the password.
Share
Related Posts

Azure DevOps Terraform Pipeline with Checkov & Approvals
Setting up an Azure DevOps pipeline for Terraform deployments with Checkov scans, validation, and manual approval steps.

Rotating Azure DevOps SSH Keys: How to Update Your Git Remotes and SSH Config
Learn how to rotate expired Azure DevOps SSH keys, update your SSH configuration, and fix Git remote authentication quickly and securely.

Generating an Azure Storage Account SAS token using Azure Logic and Function apps
Learn how to generate an Azure Storage Account SAS token from a Logic App using an Azure Function. This step-by-step guide covers deploying a PowerShell-based Function App, creating the SAS token generation function, and integrating it into your Logic App workflow. Overcome common challenges and enhance your Azure development skills with this practical tutorial.